Ocean Acidification Image. Ocean acidification is sometimes called "climate change's equally evil twin," and for good reason: it's a significant and harmful consequence of excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that we don't see or feel because its effects are happening underwater. Ocean waves off the coast of New Zealand.
The more acidic seawater becomes, the less calcium carbonate it can hold. Ocean acidification is a change in the properties of ocean water that can be harmful for plants and animals. As a consequence of acidification, marine life face a two-fold challenge: decreased. carbonate. availability and increased acidity.
The more acidic seawater becomes, the less calcium carbonate it can hold. Ocean waves off the coast of New Zealand. This is the process known as ocean acidification.
Without strong shells, the young crabs suffer damage to their sensory organs, as CNN reported. Ocean waves off the coast of New Zealand. Learn about other indicators in this section Climate Change Indicators. ocean acidification.
Without strong shells, the young crabs suffer damage to their sensory organs, as CNN reported. Scientists have observed that the ocean is becoming more acidic as its water absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Ocean acidification is sometimes called "climate change's equally evil twin," and for good reason: it's a significant and harmful consequence of excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that we don't see or feel because its effects are happening underwater.
The more alkaline the water is, the better poised it is to resist ocean acidification. (Image credit: Ifremer/ESA/CNES) Ocean acidification can now be seen from space, highlighting an ongoing. Ocean acidification is a global threat to the world's oceans, estuaries, and waterways. Learn about other indicators in this section Climate Change Indicators. ocean acidification.
Like a sponge, our oceans are absorbing increasing amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This absorption slows down global warming, but it also lowers the ocean's pH, making it more acidic. As a consequence of acidification, marine life face a two-fold challenge: decreased. carbonate. availability and increased acidity.
Learn about other indicators in this section Climate Change Indicators. ocean acidification. By taking measurements of seawater over many years. They found that the lowered pH is dissolving the shells of young Dungeness crabs in Oregon, Washington and British Columbia.
Excess carbon dioxide is having profound effects in the water, including putting shelled animals at risk. Watch our video for a quick overview. Ocean acidification is a reduction in the pH of the ocean over time, caused primarily by uptake of carbon pollution from the atmosphere due to climate change.
Excess carbon dioxide is having profound effects in the water, including putting shelled animals at risk. The main cause of ocean acidification is human burning of fossil fuels. Ocean acidification is a global threat to the world's oceans, estuaries, and waterways.
It is often called "climate change's evil twin" and is projected to grow as carbon dioxide continues to be emitted into the atmosphere at record-high levels. Ocean waves off the coast of New Zealand. Ocean acidification is a global threat to the world's oceans, estuaries, and waterways.
Learn about other indicators in this section Climate Change Indicators. ocean acidification. Watch our video for a quick overview. Ocean acidification is a reduction in the pH of the ocean over time, caused primarily by uptake of carbon pollution from the atmosphere due to climate change.
Without strong shells, the young crabs suffer damage to their sensory organs, as CNN reported. Ocean acidification is a change in the properties of ocean water that can be harmful for plants and animals. As a consequence of acidification, marine life face a two-fold challenge: decreased. carbonate. availability and increased acidity.
Excess carbon dioxide is having profound effects in the water, including putting shelled animals at risk. Noun. measure of a substance's acid or basic composition. Ocean acidification, a lowering of ocean pH, has the potential to significantly impact marine ecosystems by the.
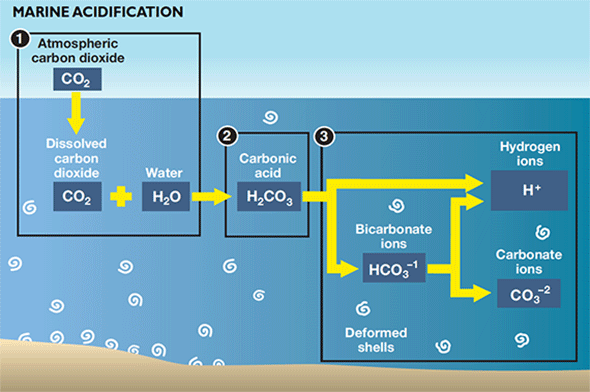
Carbon dioxide reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid. As the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases, the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the ocean also increases. By taking measurements of seawater over many years.
Ocean acidification, a lowering of ocean pH, has the potential to significantly impact marine ecosystems by the. Ocean acidification is a reduction in the pH of the ocean over time, caused primarily by uptake of carbon pollution from the atmosphere due to climate change. Ocean acidification is a change in the properties of ocean water that can be harmful for plants and animals.
Ocean acidification is weakening coral structures in the Caribbean and in cold-water reefs in waters off of Scotland and Norway.
Learn about other indicators in this section Climate Change Indicators. ocean acidification.
Carbon dioxide reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid. Excess carbon dioxide is having profound effects in the water, including putting shelled animals at risk. It is often called "climate change's evil twin" and is projected to grow as carbon dioxide continues to be emitted into the atmosphere at record-high levels.








