Ocean Acidity Image. Noun. decrease in the ocean's pH levels, caused primarily by increased carbon dioxide. Acidity is commonly measured using the pH scale.
Ocean waves off the coast of New Zealand. What makes a solution more acidic is the presence of positively charged hydrogen. They found that the lowered pH is dissolving the shells of young Dungeness crabs in Oregon, Washington and British Columbia.
What makes a solution more acidic is the presence of positively charged hydrogen. Ocean waves off the coast of New Zealand. Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well.
S. commercial fish catch and support more than. Ocean acidification is spreading rapidly in the western Arctic Ocean in both area and depth, potentially affecting shellfish, other marine species in the food web and communities that depend on these resources, according to new research published in Nature Climate Change by NOAA, Chinese marine scientists and other partners.. Associated chemical reactions can make it difficult for marine calcifying organisms, such as coral and some plankton, to form shells and skeletons, and existing shells become vulnerable to.
Pioneering techniques that use satellites to monitor ocean acidification are set to revolutionise the way that marine biologists and climate scientists study the ocean. S. commercial fish catch and support more than. Ocean acidification threatens corals and shellfish. pH.
S. shellfish industry to ocean acidification. Without strong shells, the young crabs suffer damage to their sensory organs, as CNN reported. Ocean acidification impacts on fish and seaweeds.
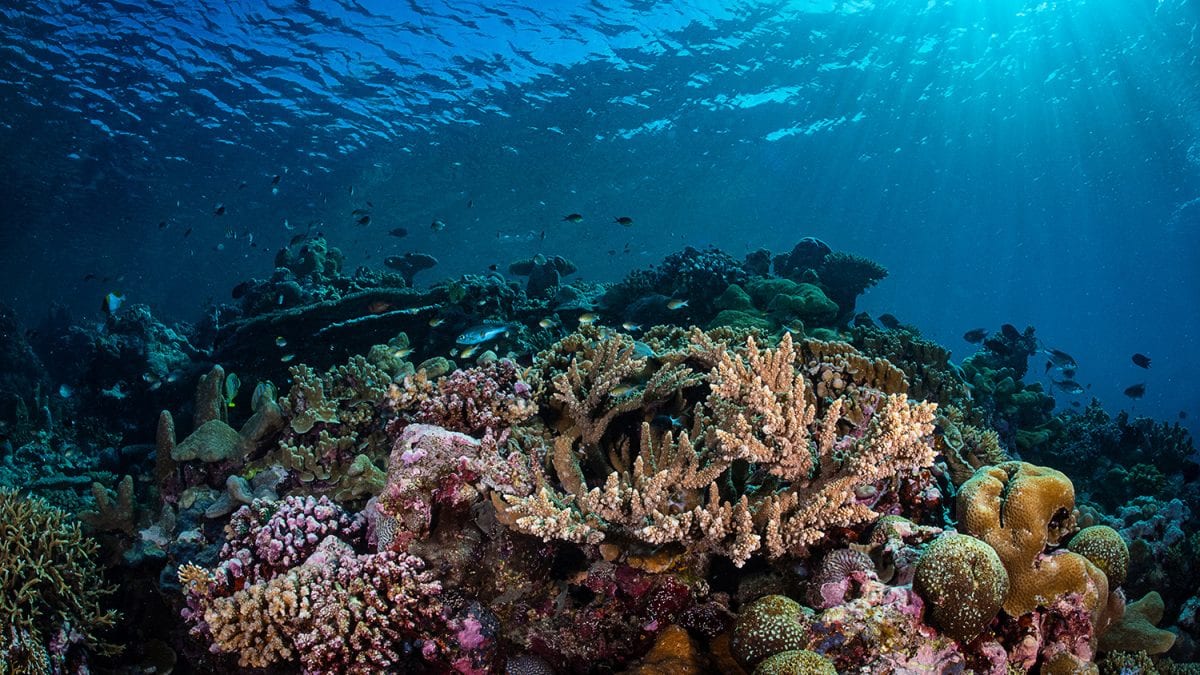
Acidity is commonly measured using the pH scale. This process, known as ocean acidification, is having negative impacts on marine animals, particularly shellfish. The lower the pH, the more acidic the substance.
The international team of scientists published some of their early findings and images in the journal Environmental Science and Technology today. Ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the pH of ocean water, caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but also by other chemical additions or subtractions from the ocean.. of pteropods and other calcium-secreting organisms will be reduced due to the effects of dissolved carbon dioxide on ocean acidity. Studies have shown that decreased pH levels also affect the ability of larval clownfish to locate suitable.
Because the pH scale is logarithmic, a difference of one pH unit represents a tenfold acidification. The lower the pH, the more acidic the substance. What makes a solution more acidic is the presence of positively charged hydrogen.
Pioneering techniques that use satellites to monitor ocean acidification are set to revolutionise the way that marine biologists and climate scientists study the ocean. The lower the pH, the more acidic the substance. We play an important role in monitoring the conditions and health of marine waters.
Data used is adapted from published data, but how it is adapted is not specified. Top: Pteropod snails, which live in the California Current System, are especially sensitive to ocean acidification. They found that the lowered pH is dissolving the shells of young Dungeness crabs in Oregon, Washington and British Columbia.
Ocean acidification refers to a reduction in the pH of ocean water, caused primarily by uptake of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but also by other chemical additions or subtractions from the ocean.. of pteropods and other calcium-secreting organisms will be reduced due to the effects of dissolved carbon dioxide on ocean acidity. Ocean water is becoming more acidic because of carbon pollution from human activities. They found that the lowered pH is dissolving the shells of young Dungeness crabs in Oregon, Washington and British Columbia.
Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well. Pioneering techniques that use satellites to monitor ocean acidification are set to revolutionise the way that marine biologists and climate scientists study the ocean. Top: Pteropod snails, which live in the California Current System, are especially sensitive to ocean acidification.
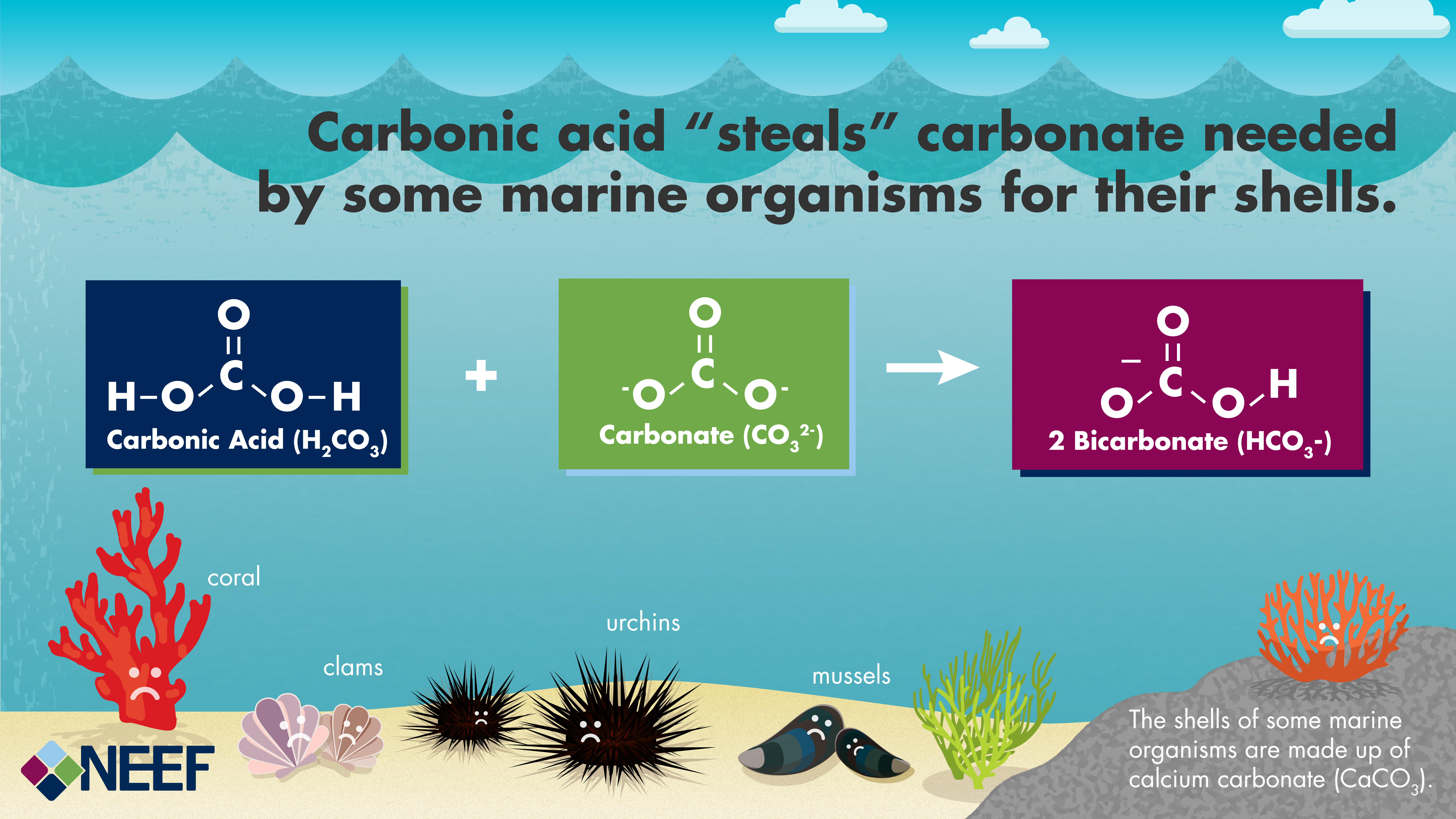
Because the pH scale is logarithmic, a difference of one pH unit represents a tenfold acidification. As a consequence of acidification, marine life face a two-fold challenge: decreased. carbonate. availability and increased acidity. Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well.
Data used is adapted from published data, but how it is adapted is not specified. Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well. The more alkaline the water is, the better poised it is to resist ocean acidification. (Image credit: Ifremer/ESA/CNES) Ocean acidification can now be seen from space, highlighting an ongoing.
This image shows its effects, including ragged, dissolving shell ridges on upper surface, a cloudy shell in lower right quadrant, and severe abrasions. (Credit: NOAA Photo Library / CC) Bottom: In laboratory experiments, this. Ocean acidification impacts on fish and seaweeds. Because the pH scale is logarithmic, a difference of one pH unit represents a tenfold acidification.
Acidity is commonly measured using the pH scale.
Ocean water is becoming more acidic because of carbon pollution from human activities.
Data used is adapted from published data, but how it is adapted is not specified. Visualization is presented with very little background information or context. Noun. measure of a substance's acid or basic composition.